You’re tired but you can’t sleep. Or you always wake up in the middle of the night. What can you do to go to bed?
Sleep problems can affect your health and well-being. But we can help you hit the sack right away!
Continue reading to find out why you can’t sleep and our tips for getting better sleep, from making healthy changes in your lifestyle to changing your mattress and pillow.
You might be interested in: Understanding Natural and Unnatural Sleep Aids
Why You Can’t Sleep at Night
There are several causes of lack of sleep at night. Here are some of them.
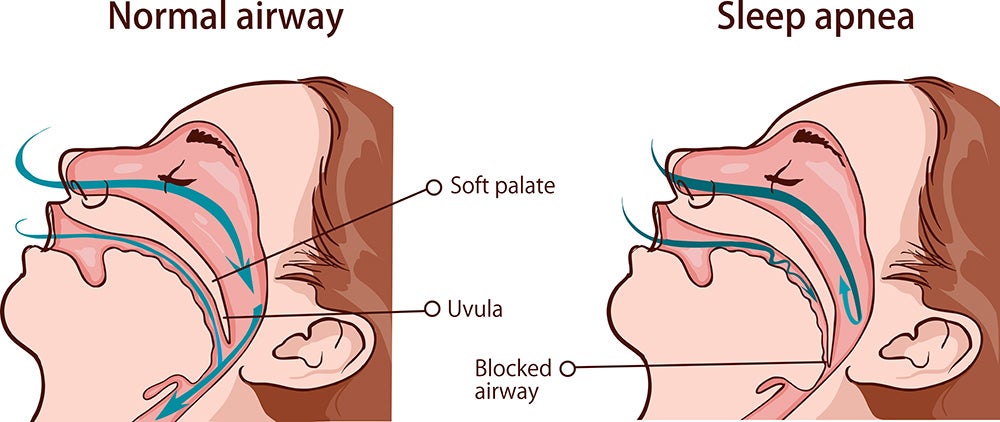
— Sleep Apnea
You might not be able to sleep because you have sleep apnea, an alarming sleep disorder where breathing is interrupted during bedtime. Breathing stops and starts while sleeping, leading to loud snoring and exhaustion in the morning. Sleep apnea can cause heart conditions and high blood pressure if left untreated.
— Stress
Stress is normal because it serves as a natural response to dangerous situations. However, too much can lead to an increased state of arousal that can severely impact your sleep. Rapid, depressing, and anxious thoughts can hinder sleep, and not enough sleep can lead to further stress.
— Health Issues
Aside from insomnia, other health conditions like dementia, depression, diabetes, and musculoskeletal disorders can disrupt your sleep. For example, the intense pain caused by arthritis can make dozing off difficult. Spikes in blood sugar levels can also result in night sweats.
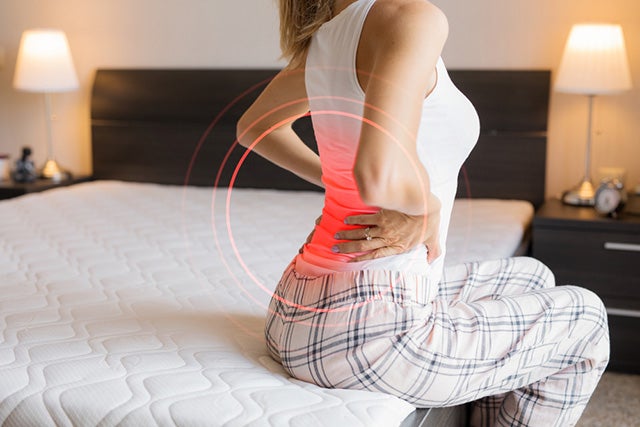
— Poor Mattress
Body pain can lead to sleep deprivation and may worsen if you have the wrong mattress. If your mattress does not give enough support for your sleeping posture, then it’s time to get a new one. If it doesn’t meet the level of comfort you want, you’re going to wake up every day tired and sore.
A medium-firm mattress will keep your spinal alignment neutral and will relieve pressure points.
— Injury
Certain chemicals in the body help us fall asleep, but an injury can change these chemical processes. For instance, the internal clock alters, anxiety worsens, and serotonin production is inhibited. These typically occur in people who suffer from traumatic brain injury (TBI). Studies also show that TBI patients are three times more prone to sleep disorders.
— Sleeping Partner
Some people find it hard to sleep in bed with someone because the small space makes them feel uncomfortable. You may also have trouble traveling to dreamland if your partner snores! If this is the case, use a pillow to elevate their head and let them turn to the other side. If your partner moves a lot, get a mattress for couples with optimal edge support.
— Medications
If you take one of the following medications, you are more likely to have sleep disruptions:
- Anticonvulsant
- Appetite suppressants
- Beta agonist
- Cold medicine
- Diuretics
- Dopamine agonists
- Medications that lower blood pressure
- Niacin
- Psychostimulants and amphetamines
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or antidepressants
- Steroids
- Theophylline.
— Poor Lifestyle
Your bad habits can cause sleep deprivation. Some lifestyle factors include:
- Drinking alcohol
- Overusing smartphones, computers, or television before bedtime
- Drinking too much caffeine every day or close to bedtime
- Exercising at night
- Odd working hours
You may want to read: Natural Sleep Aids For A Better Night’s Sleep
How Sleep Deprivation Affects You
Poor sleep can trigger or worsen your physical, mental, and emotional health issues. Here are the potential effects of sleep deprivation on your body.
— Physically
Sleeplessness can contribute to different health problems including:
- Immune system. Your immunity can be compromised in that you are more prone to infections and respiratory diseases. It is also associated with a poor response to vaccines. Note that your immune system will never get used to lack of sleep, so these conditions may be chronic in the future.
- Diabetes. An inadequate amount of sleep can cause an inability to regulate your blood sugar levels, contributing to diabetes.
- Heart diseases. Studies show that insufficient sleep can lead to cardiovascular issues like coronary heart disease, high blood pressure, stroke, and heart attack.
- Weight gain. Studies show that people eat more carbs and calories when they experience sleep deficiency. Poor sleep also makes it hard to lose weight.
- Hormonal imbalance. Because sleep aids in producing normal hormone levels, lack of sleep can result in hormonal imbalance.
— Mentally
Your mind can also be affected in many ways if you experience sleeplessness.
- Lack of sleep can slow down the thought process. It can reduce your alertness and concentration in the morning, so you are unable to work more efficiently.
- Sleep deficiency harms your memory because the nerve connections that produce memories are weakened. Different sleep phases have their roles in keeping memories. That is why you often misplace things when you’re sleepy.
- Inadequate sleep makes learning more difficult. Because you can’t concentrate properly, you can’t process information and acquire the needed knowledge and skills.
— Emotionally
Sleep deficiency can affect your mood and overall emotional health. It can make you angrier and more irritable because you are unable to deal with stress. Even partial sleep deprivation can lead to loneliness, stress, and exhaustion.
Your psychological state can also be affected by sleeplessness. You can develop depression and anxiety when you don’t sleep well enough because the cortisol levels increase and the serotonin and dopamine are inhibited. Studies show that around 15-20% of people with insomnia are more likely to be diagnosed with depression.
Sometimes, it’s the other way around. Difficulty sleeping can be a symptom of depression. Negative thoughts due to personal problems can make you stay up all night.
This means lack of sleep and psychological conditions affect one another.
What to Do When You Can’t Sleep
So you want to sleep but your body won’t let you. Try these strategies to fall asleep fast!
• Exercise
Exercise can effectively improve your sleep and reduce insomnia-related symptoms compared to sleeping pills and supplements. Studies show that older adults found exercise to reduce the time it takes for them to sleep in half.
But exercise before bedtime is not recommended. It can cause the opposite. Exercise can stimulate your whole body and make you alert. But some report no negative effects of exercising before sleeping.
• Reduce Alcohol and Caffeine Intake
Caffeine is a stimulant that can make it difficult to sleep. Reduce your caffeine intake to two cups per day, and stop drinking coffee a few hours before bedtime.
Alcohol can also interrupt your sleep. While it is a sedative that can make you fall asleep, it can ruin your sleep cycle in the future and cause non-restorative sleep.
• Tea
Here are the best bedtime teas to try:
- Chamomile tea is a sedative that can improve the quality of sleep, especially among older adults. It has antioxidants that reduce anxiety and keep you calm.
- Valerian root can treat insomnia, depression, anxiety, and symptoms of menopause.
- Ashwagandha tea is an alternative medicine that can calm the nerves and inhibit excited responses.
- Lemon balm tea comes from the family of mint to improve one’s mood and prevent insomnia symptoms.
- Passionflower tea is found to improve your rest compared to the placebo group.
• Massage
Massage can enhance your sleep by reducing your stress and managing any pain. Massage reduces your cortisol levels or the hormone associated with stress. It also increases dopamine and serotonin, which are responsible for mood stability.
Sleep deprivation can worsen any type of pain you have, but a massage is an effective treatment for headaches, arthritis, and back and neck pain.
These effects can help with sleep disorders like insomnia, narcolepsy, and sleep apnea.
You may also try alternative therapies like acupuncture, acupressure, and tai chi. However, there are not enough studies to prove that these forms of massage work.
• Therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy is a type of therapy that helps transform your pre-bedtime behavior by changing the thoughts that keep you from falling asleep. Compared to sleeping pills, CBT can solve the root cause of your sleep problems.
Different techniques can be used depending on your needs, such as stimulus control therapy, sleep restriction, relaxation training, or staying passively awake. The best approach is a combination of these approaches.
Therapy is for everyone! Whether you are diagnosed with a sleep disorder or not, you are welcome to try it. It can be done per individual, by group, or online.
• Reduce Blue Light at Night
Exposure to light during the evening disrupts your circadian rhythm, making your brain believe that it’s still morning. Blue light is the worst kind of light that affects your sleep quality. It is released by electronic devices such as computers, televisions, and smartphones.
Here are some ways to avoid blue light exposure during the night:
- Wear anti-blue light glasses
- Change your light bulb to a dim red one.
- Turn off any bright light 2 hours before bedtime.
- Stop watching TV 2 hours before sleeping
- Install smartphone apps that block blue light.
- Set an alarm before sleeping to be reminded to stop using your gadgets.
• Reduce Long Daytime Naps
Power naps might help save energy during the day, but too much can negatively affect your sleep at night. Irregular sleep during the daytime can make your body clock confused. Some get sleepier during the day than at night.
If you can’t help taking nap times, make sure to keep them short at 30 minutes or less. This is enough to boost your brain function. Longer daytime naps can affect the quality of your sleep and your health in general.
If you still sleep well while taking regular naps in the morning or afternoon, you shouldn’t worry.
• Relaxation Techniques
Controlled breathing is one example of a relaxation technique that can reduce stress in the central nervous system and help the brain fall asleep. Slowly inhale through your nose and exhale using your mouth. Count every breath until you feel sleepy.
Progressive muscle relaxation is another technique that tightens the muscles and releases them. Simply breathe in and out as you tense your facial muscles for ten seconds. Once you feel pressure, release the muscles and breathe in and out again. Tense and release your shoulder down to the stomach, arms, legs, and feet while inhaling and exhaling.
You may want to read: Melatonin: A Natural Sleep Aid Worth Considering
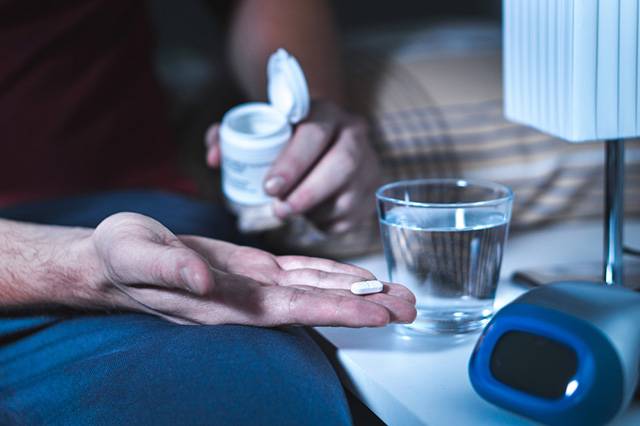
• Sleep Aids
Melatonin is a sleeping hormone that may come in the form of supplements to signal the brain to relax and sleep. This sleep aid is deemed as the easiest way to treat insomnia with various studies supporting it. Those who travel to a new time zone also use melatonin to adjust their body clock.
This sleep hormone is available over the counter in some countries without withdrawal effects. But some countries require a prescription.
You can take 1-5mg of melatonin a few minutes before bedtime. Speak to your doctor about using melatonin for your child!
You may want to check out: The Pros and Cons of Taking Sleeping Pills
• Try Other Supplements
Aside from melatonin, here are other supplements that can help you relax and sleep better.
- Ginko Biloba reduces stress, promotes relaxation, and aids sleep if you take 250mg one hour before sleeping.
- Magnesium can help you relax and sleep better.
- Valerian root can help you sleep faster if you take 500mg before bedtime.
- L-theanine is an amino acid that can be consumed at 100-200mg before sleeping to help you sleep.
- Lavender is an herb that can be taken in the form of tea or be used as aromatherapy to calm you down and improve your sleep.
- Glycine deepens your sleep. Take 3 grams of this amino acid for maximum benefits.
• New Mattress
An improved mattress can give you a better night’s sleep if you’ve been struggling to sleep in your desired position because of body aches and pain. Some can’t sleep because their mattress feels like they’re falling off the bed, sinking in, or being bounced up and down. Others have mattresses that can’t regulate temperature.
Studies show that the best kind of mattress is one that offers comfort, firmness, and spinal alignment during bedtime. These qualities are often found in a medium-firm mattress.
Don’t be in a rush when finding the right mattress. Look for companies that offer long sleep trials, specifically 90 days or more.
• New Pillow
Maybe your mattress isn’t the problem, but your pillow. It can be a direct source of headache, neck pain, and spine issues.
If you’ve been getting out of bed with a painful neck and shoulders, consider getting a new pillow with premium filling. Memory foam, for instance, gives personalized support by relieving pressure points on the neck and head. Down filling is made of fine down feathers for adequate sinkage.
Another factor to consider when getting a new pillow is firmness. Back and stomach sleepers need soft pillows, while side sleepers with neck pain may benefit from very firm pillows.
• New Sheets
Your bed sheets may not be the main reason for your pain and discomfort while sleeping, but they can contribute to a cozier and comfortable sleep! Our body releases heat at night, so we must choose bed linens that do not trap heat to avoid sweating and sleep interruptions.
Bamboo, linen, and cotton are the best choices for moisture-wicking, natural materials. A thread count of 200-400 is ideal for tropical climates and the summer season, while a sheet thread count of over 400 can be used for winter.
Pair the bed sheet with a good pillowcase made of silk for a more luxurious sleeping experience.
• New Comforter
Your comforter may be too thin to give the warmth you need at night. Try getting a separate comforter instead of a 2-in-1 cover and blanket because it is thicker and more comfortable. Some factors to take into consideration when getting a new comforter include the fill material, fill power, stitching, and the outer fabric.
Down is the most common fill material because it keeps you warm without feeling heavy. It’s also more breathable. In case you feel warm in bed, you won’t sweat too much with this comforter type.
Fill power refers to how fluffy the filling is. Here’s a guide for you:
- Below 400: for summer
- 400-600: works any time of the year
- 600-800: for winter
- 800 and up colder winter nights.
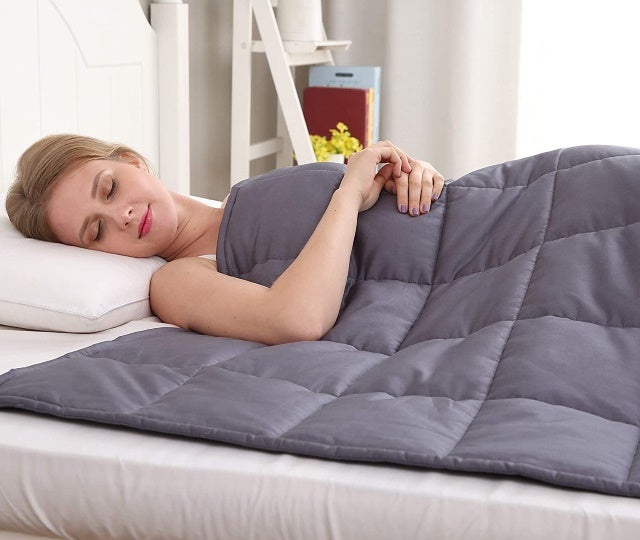
• Weighted Blanket
A weighted blanket promotes the so-called deep pressure stimulation to keep you calm through its firm pressure. It is said to stimulate serotonin, the happy hormone while decreasing cortisol, the stress hormone. It can also increase your melatonin levels for improved sleep.
Weighted blankets can also ease anxiety which often interrupts your sleep. The evenly weighted pressure on your body hinders the fight-or-flight response and relaxes your nervous system.
People with Autism can also benefit from the touch of a weighted blanket. It activates the tactile sense to avoid other sensory stimuli.
Sleep Better through a Holistic Approach
Lack of sleep may be caused by an underlying medical condition, poor sleeping environment, bad bedding, and a poor lifestyle. If left unresolved, it can have a detrimental effect on your physical, emotional, and mental health.
Consider all aspects when trying to get a good night’s sleep:
- Develop good health habits like exercising regularly, taking supplements, and having a balanced diet
- Improve your bedroom environment by dimming the lights and changing your mattress, pillows, and sheets.
- Rule out any sleep disorder or health condition.
The Bottom Line
Sleep deprivation can cause a slew of health issues. It’s good to try whatever you can to get to sleep. We hope these tips have helped you out. Be sure to let us know in the comments below. And for more sleep tips, check out our guide to creating a sleep schedule.
Photo credit: Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock; fizkes/Shutterstock;
Kaspars Grinvalds/Shutterstock; Rawpixel.com/Shutterstock;
Syda Productions/Shutterstock; Tero Vesalainen/Shutterstock;
r.classen/Shutterstock; fizkes/Shutterstock;
Gorodenkoff/Shutterstock; vladimir salman/Shutterstock;
Realstock/Shutterstock; Elena Kotova/Shutterstock;
Tero Vesalainen/Shutterstock; dturphoto/Shutterstock;
Iakov Filimonov/Shutterstock; New Africa/Shutterstock;
JulieK2/Shutterstock; Stock-Asso/Shutterstock