Getting a good night’s sleep is important for maintaining your health and a healthy lifestyle. However, there are many factors that can compromise the quality of your sleep, which can, in turn, affect your health and overall quality of life.
One such issue that can hinder the quality of sleep a person receives is sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is a sleeping disorder that causes a person to have pauses in their breathing or moments of shallow breathing. This means that people who suffer from sleep apnea stop breathing repeatedly during their sleep and if left untreated it may even occur hundreds of times a night. This can be extremely dangerous, as it means that the brain, as well as the rest of the body, might not receive enough oxygen.

Different Forms of Sleep Apnea
There are two different forms of sleep apnea, these are known as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea. There are certain differences between these two different types of sleep apnea that make their treatments and symptoms different. Let’s take a deeper look at the two different forms of sleep apnea.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
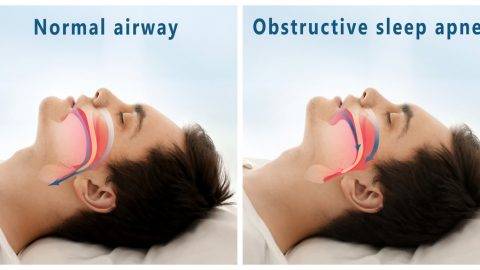
Central Sleep Apnea

The brain’s respiratory control centers are imbalanced, which means that the carbon dioxide levels in the blood which are monitored by a neurological feedback mechanism do not respond fast enough to maintain a consistent rate of respiration. The breathing system cycles between apnea and hyper apnea, where breathing happens at a faster rate to compensate for the pauses in breathing.
During periods of central sleep apnea, the sleeper stops breathing and then starts again, there is no effort made to breathe, there are no chest movements or struggles to breathe. This is dangerous as extended periods of not breathing can lead to many complications such as not enough oxygen reaching the brain and the rest of the body.
Stages of Sleep
There are two major different stages of sleep which are known as REM sleep and non-REM sleep. REM stands for rapid eye movement, which means that our eyes move very quickly in different directions. This rapid movement of the eyes does not happen in non-REM sleep. REM sleep is the deeper form of sleep and when dreams occur, in this stage the brain looks similar to the way it would when you are awake.
Due to the fact that REM sleep is the deeper form of sleep the muscles are more relaxed. Although sleep apnea can occur during any stage of sleep, it most often occurs during the REM stages of sleep and it is typically worse during that stage. This is because especially the muscles in the upper airway are further relaxed naturally during the REM stage of sleep. It is due to this fact that many individuals only suffer from sleep apnea in REM sleep.
Stages of Non-REM Sleep
Prior to reaching the deeper stage of REM sleep, an individual passes through three different non-REM sleep stages. Depending on the severity of sleep apnea, it can occur during these stages of sleep as well.



Conclusion
Overall sleep apnea has two different forms and if untreated it can be quite dangerous to the health of a person. Although sleep apnea can occur in any stage of sleep it is most likely to occur during the deeper stages of sleep which includes REM sleep. Hopefully, this article was able to shed some light on sleep apnea and the stages of sleep it occurs in.