Perhaps you’ve slept with someone who snores in their sleep, or maybe you’re the culprit in this case. Whatever the situation, everyone has had a brush with snoring to understand it’s not fun. In some cases, snoring can become so loud that it disturbs the sleep of others and the snorer himself.
Naturally, when this disturbance occurs in your life, two basic questions come to mind; why are you snoring, and what can you do to treat it?
You might want to check: How Overcome Your Snoring?
Why Do People Snore?

In some cases, snoring is an innocent one-time occurrence that could complement a cold or flu, or simply be due to an intense, tiring day.
Simpler, less harmful, and controllable reasons behind why you snore are listed below.
- The anatomy of your mouth or nose could be the prime reason why you snore. People who have narrower passages will have a greater chance of snoring since air flows very close to the tissues on the side of the throat.
- Being ill due to a cold or flu. With sicknesses that involve congestion within the nasal passages, there is a greater chance of snoring since your nasal passages are clogged.
- Nightly allergies can also be the prime cause of your snoring, which could mean hypoallergenic bedding is the way to go.
- Alcohol consumption and rapid weight gain can create a narrower and coarser throat at night. You’ll have more loose tissues which will vibrate when air flows through your mouth and nose.
- More chronic nasal conditions such as crooked partitions and internal blocks will cause snoring and could lead to trouble breathing at night.
- Regular sleep deprivation could lead to breathing with your mouth open. This naturally brings forth greater airflow intake and more chances of a dry throat with loose tissues.
- Finally, there is the sleep position. Most people who snore sleep on their back. This is because gravity plays a greater role in the pressure over your throat.
You might be interested: Best Pillows for Snoring
What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (also commonly referred to as OSA) is a sleeping disorder that is primarily spotted when you begin to snore routinely.

The incapability to breathe properly at night will eventually begin to wake you up during the night, either snorting or gasping for air. This kind of disturbance takes a while to recover from and can develop into a habit of light sleeping.
The effects of disturbed sleep then follow and will be discussed later on in the article.
Symptoms to Detect OSA
- You have significant pauses in breath at nighttime. These are periods where your breathing either slows down or stops completely.
- There is an increased lack of concentration during the day when performing tasks.
- You can wake up to morning headaches which can last at least an hour or so. If they begin to build up on top of one another, then perhaps the whole day.
- You could also wake up with a sore throat from the coarse inflow of air or persistent dryness.
- Since you’ll be sleeping lighter, there is also a chance of restless sleep. Continuous nights with little to no consecutive sleep could harm the rest of your productive day.
- You can end up with high blood pressure levels.
- There can be chest pains during the night due to the lack of airflow, and possibly more in the day as an after-effect of inconsistent sleep.
- For children, other detectable symptoms are poor attention span, numerous behavioral issues with aggression and concentration, and a poorer performance in school.
If you feel that you have dealt with any of the symptoms listed here, then it’s highly recommended to see a doctor to confirm whether or not you’re suffering from OSA. If it’s your child who has experienced all or any of these symptoms, then first consult with your pediatrician before taking any action.
You might want to read: How Do You Stop Snoring?
When is Snoring Harmful?
Most of the time, snoring is nothing more than a nuisance that is dealt with occasionally or routinely. There is no harm in someone snoring when it doesn’t disturb their sleep, other than their partner who may be interested in a pair of earmuffs.
It’s when snoring starts to disrupt your sleep, causing you to wake up continuously, having a hard time breathing, that you need to seriously consider professional treatment.

Behavioral changes and complications can occur such as frequent frustration, aggressiveness, and lack of concentration or capability to learn.
In the worst of scenarios, OSA can lead to higher blood pressure ratings, chronic heart conditions, or even result in a stroke. The lack of proper sleep will create daytime grogginess which could increase the risk of accidents if you have to drive early in the morning.
You might want to check: Best Anti-Snoring Devices
What are Ways to Treat Snoring?
Before you indulge in finding a solution to your snoring dilemma, it’s important to consult a sleep or health professional who can provide you with a proper diagnosis and plausible treatment.
For snorers who are not suffering from OSA but simply a mild inconvenience, there are easy ways to repair this issue at home with healthy habits.

OSA Treatment
If you suffer from OSA, then there are more severe treatments required to cure this sleep disorder.

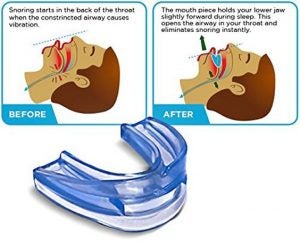
Side effects of this treatment are extreme salivation which potentially results in a dry mouth in the morning. You may experience facial discomfort since you won’t be used to sleeping with these appliances in your mouth.
During this process, you’ll be working with your dental and sleep specialist to ensure this doesn’t create too many side effects or that it harms more than it benefits you.
Oral appliances are form-fitting dental mouthpieces to position your jaw, tongue, and soft palate so your air passages are open. You may need dental work at least once every six months, working with your dental and sleep specialist to make this work.
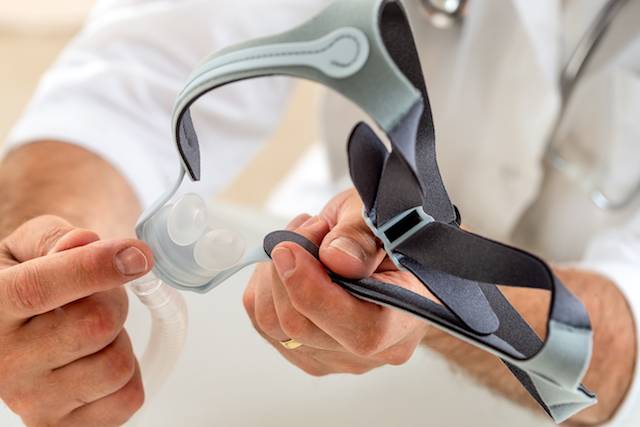
Another treatment to attempt is Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. With this treatment, you wear a mask over either your nose or your mouth whenever you sleep. This mask is connected to a machine that dispenses pressurized air to you while you sleep to keep your passages wide open.
Of course, quite like the oral appliances, this will take some getting used to since it’s not easy to sleep with a mask on in the presence of a machine.

UPPP is uvulopalatopharyngoplasty surgery, in which anesthetics are used to subdue the patient, and hanging or loose tissues are trimmed off. This will improve sleep as there is nothing for air to brush against while you sleep.
The MMA procedure is called the maxillomandibular advancement in which your upper and lower jaw are moved forward. This helps open the airway and allow for greater space and ease when breathing at night.
The Radiofrequency Tissue Ablation procedure uses low-intensity radiofrequency signals to subtly shrink the tissue located in your soft palate, tongue, throat, or nose. The smaller they are, the less chance there is of them vibrating at night.
Conclusion
For many people, snoring is a nightly disturbance that wakes them and their partner, regardless of whoever is snoring. This can lead to some very groggy days and long-term consequences.
If it’s not a serious issue, then there are normal habits you can build to prevent snoring in the future. If your snoring is a result of a clinical condition, then it’s best to consult a doctor, receive a diagnosis, and work your way from there to get proper treatment.
Photo credit: JPC-PROD/Shutterstock; Chu KyungMin/Shutterstock