Do you often wake up feeling tired and day-to-day tasks seem more like chores? It could be that you’re not getting enough sleep. What some people fail to understand is that sleep deprivation is more than just dreaming about your bed and feeling drowsy. It can lead to a series of health threats and could put your life in danger. Learn to read the signs of lack of sleep and fight them.
You might want to read: Health Benefits Of Sleeping And How Far They Reach
How Much Sleep Do We Need?
The findings of several scientific studies make it abundantly evident that getting enough sleep is crucial at any age. Sleep not only recharges the body but also strengthens practically every other system in the body, including the brain. But how many hours of sleep do we need to acquire to take advantage of these advantages?
According to the National Sleep Foundation, an average healthy adult needs between seven and nine hours of sleep per night.
To facilitate their growth and development, infants, young children, and teenagers require an increased amount of sleep. Those who are above the age of 65 should also aim for seven to eight hours of sleep each night.
— Age
The amount of sleep a human requires is also based on their age. Growing children and teens need more sleep than adults. According to the CDC, here is how much you need to sleep every night based on your age:
- Newborns between 0 and 3 months need about 14 to 17 hours of sleep daily.
- Infants from 4 to 12 months need 12 to 16 hours.
- Toddlers aged between 1 and 2 years require 11 to 14 hours.
- Preschoolers between 3 and 5 years need 10 to 13 hours.
- Children between the ages of 6 and 12 years need 9 to 12 hours of sleep.
- Teens between 13 and 18 years of age need 8 to 10 hours of sleep.
- Adults up to the age of 64 can make do with 7 to 9 hours of sleep.
- Elders beyond the age of 65 need 7 or 8 hours of sleep.
— Gender
When compared to men, women require a greater total amount of sleep, although the exact number of hours required has not been determined by studies. For adults to maintain their best possible health, they must get at least seven hours of sleep each night.
But when it comes to the disparities in sleep, studies indicated that women tend to receive more sleep than men by 11 to 13 minutes. This difference can be attributed to the fact that women tend to fall asleep faster than men.
Do Women Need More Sleep Than Men?
There are some possible explanations for why women may have a greater demand for sleep than males. Insomnia affects women at a rate that is 40 percent higher than that of males.
Both anxiety and depression are strongly linked to sleeplessness and women are nearly twice as likely as men to suffer from both diseases. Also, females are nearly twice as likely to suffer from insomnia as males.
People who suffer from insomnia have trouble falling asleep or difficulty staying asleep, and they also struggle with daytime tiredness as a result of their condition.
Another factor that contributes to the greater demand for sleep that women have compared to males is hormones. The cycles of sleep and wakefulness that we experience are governed by our hormones. These hormones play a role in determining when we feel fatigued, hungry, alert, and in many other ways as well.
Hormonal shifts occur monthly and throughout a woman’s lifetime, and these shifts have an effect on her circadian rhythms and make her require more sleep.
— Menopause
Up to 85 percent of women go through menopause with hot flashes. When these things happen in the middle of the night, ladies wake up in a cold sweat, which disrupts their sleep.
During menopause, a woman’s already elevated risk of getting sleep apnea can become even more severe. Even if the individual does not wake up as a result of the breathing interruptions caused by this sleep disorder, the quality of their sleep may be negatively impacted.
As a consequence of this, women who have sleep apnea may wake up feeling less refreshed than usual, and they may also struggle with fatigue and excessive daytime fatigue.
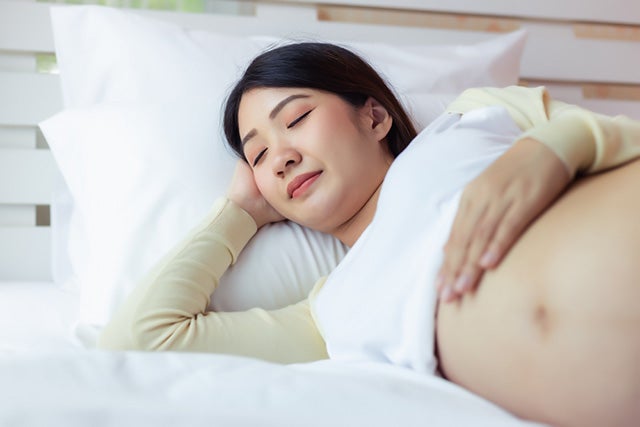
— Pregnancy
Pregnant people have an increased risk of developing a disease known as restless legs syndrome, which makes it more difficult for them to fall asleep. They are also more prone to suffer from conditions such as depression, sleep apnea, discomfort, and incontinence, all of which prevent them from getting a good night’s rest.
These sleep problems can continue into the postpartum period when the woman’s hormone levels decline at the same time that she begins caring for a newborn with an inconsistent sleep cycle, which frequently results in even more daytime sleepiness for the woman.
Dangers of Lack of Sleep
Sleep deprivation will compromise your mental health and immune system. From those points on, the quality of life starts degrading and you will experience more and more health problems.
While the short-term effects of lack of sleep are manageable, this is a problem that shouldn’t be allowed to get out of control. The unfortunate long-term effects of serious sleep deprivation are dangerous up to the point where they become life-threatening.
• Compromised Immune System
While you are unconscious, your immune system generates defensive molecules that fight infections, such as cytokines and antibodies. These compounds are employed by it in the fight against alien adversaries like viruses and bacteria.
In addition, certain cytokines improve the quality of sleep, which in turn boosts the effectiveness of your immune system to protect your body from illness.
With not enough sleep, your immune system won’t have the chance to strengthen itself. A lack of sleep causes your body’s incapacity to ward against intruders, and it also makes it difficult to recover from a disease. If you do get enough sleep, however, your body will be able to do both of these things.
Sleep deprivation for a prolonged period raises the individual’s chance of developing chronic illnesses such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
• Problems with Your Cardiovascular System
Sleep has an immediate impact on how healthy your heart and blood vessels are. In addition to this, it is critical to the body’s ability to heal and restore the cardiovascular system, particularly the blood arteries and the heart.
Insufficient sleep has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease in both men and women. Increased risks of stroke and heart attack were shown to be associated with sleeplessness, according to one study.
• Disfunctional Digestive System
Lack of sleep is a risk factor for being obese, in addition to eating an excessive amount and failing to engage in physical activity. The levels of the hormones leptin and ghrelin, which are responsible for regulating feelings of hunger and fullness, are influenced by sleep.
Your brain receives the message that you’ve eaten enough to eat from leptin. When you don’t get enough sleep, your brain produces less leptin and more ghrelin, which is a hormone that makes you feel hungry. The fluctuation of these hormones may help to explain why people eat late-night snacks or why some people overeat later on in the evening.
Sleep deprivation can make you feel too fatigued to exercise. A decrease in physical activity can lead to weight gain over time because it prevents you from burning enough calories and preventing you from gaining adequate muscle mass.
Insomnia has the additional effect of causing your body to secrete less insulin in response to meals. Your glucose level can be lowered by insulin assistance.
Lack of sleep lowers the body’s tolerance for glucose and is connected with insulin resistance. Sleep deprivation also increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. These disturbances can put a person at risk for developing diabetes mellitus and obesity.
• Respiratory Issues
There is reciprocity in the interaction that exists between your respiratory system and sleep. Your sleep may be disrupted and your overall quality of sleep may suffer if you have obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a respiratory disorder that occurs during the night.
When you wake up during the night, you’re more likely to suffer from sleep deprivation because you might find it difficult to go back to sleep. This makes your body more vulnerable to respiratory infections.
• Hormone Imbalance
Hormone production is depending on your sleep. You need at least three hours of unbroken sleep to produce testosterone, which is about the length of time that it takes to watch your first R.E.M. episode. It’s possible that getting up multiple times during the night will mess with your hormone production.
Additionally, this disruption may affect the generation of growth hormones, particularly in children and teenagers. In addition to their roles in other aspects of growth, these hormones are crucial in the process by which the body adds muscle mass and repairs damaged cells, tissues, and organs.
The pituitary gland secretes growth hormone at various points during the day, but getting enough sleep and working out also contribute to the production of this hormone.
• Central Nervous System Impact
The information that travels throughout your body is carried primarily through your central nervous system. Insomnia, especially if it’s persistent, can throw off how your body normally receives and processes information, even though sleep is essential to maintaining optimal function.
Sleep deprivation has a deleterious effect not only on your cognitive capacities but also on your emotional condition. You might experience increased impatience and a greater propensity for mood changes. It also has the potential to hinder the creative process and decision-making processes.
Your brain creates new connections between nerve cells (neurons) while you are sleeping, which assists in the consolidation of newly acquired knowledge and information. Your brain will become weary if you don’t get enough sleep, and as a result, it won’t be able to carry out its functions as well.
How Lack of Sleep Affects the Body
Now we’ve got a better picture of what sleep deprivation causes to different systems throughout your body, let’s take a more exemplified look at what can happen when you don’t get enough sleep. What does sleep deprivation do to your body, exactly?
• Can Cause Microsleep
People are likely to experience brief periods of sleepiness during the day. During these episodes, you will be unaware that you have fallen asleep for a few seconds up to many minutes at a time.
You do not have any control over microsleep, which makes it exceedingly hazardous if you are behind the wheel. If you operate heavy machinery at work and experience an episode of microsleep while doing so, you put yourself at a greater risk of being injured.
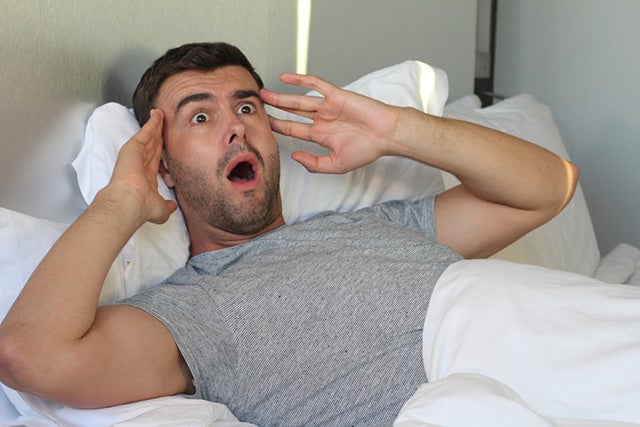
• Might Cause Hallucinations
If you go without sleep for an extended period, you run the risk of developing hallucinations, which are described as the experience of seeing or hearing things that aren’t present. People who suffer from bipolar mood disorder are more likely to experience manic episodes if they do not get enough sleep.
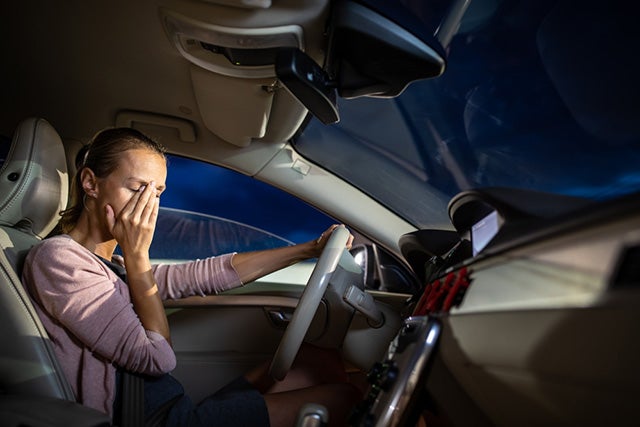
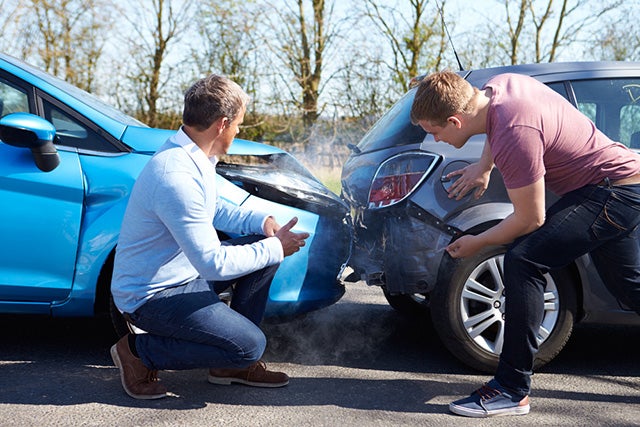
• You’re Likelier to Be in an Accident
However, a lack of sleep poses a significant threat to the general public’s safety every day on the road. It’s possible that being sleepy can reduce your reaction time just as much as being inebriated.
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration states that weariness is a factor in 100,000 car accidents and 1,550 deaths that are the direct result of car accidents each year in the United States. The issue is more prevalent among those who are younger than 25 years old.
According to several studies, not getting enough sleep and having poor-quality sleep both contribute to accidents and injuries that occur on the job. One study showed that employees who reported severe daytime sleepiness were considerably more likely to have accidents at work, particularly mishaps that occurred repeatedly. They also experienced a higher number of sick days for each mishap.
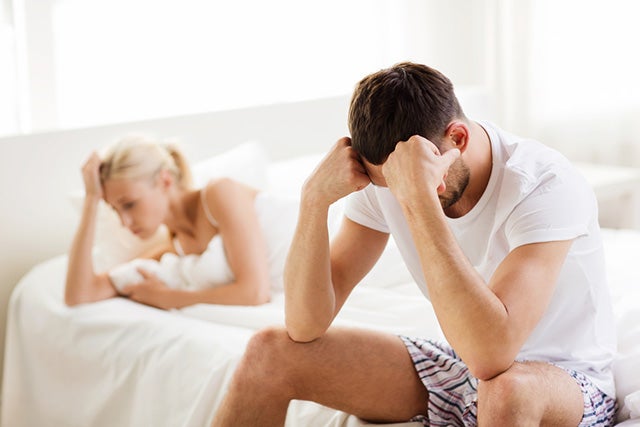
• It Lowers Your Sexual Appetite
The sleep experts claim that people who don’t get enough of it report having decreased libidos and in having sexual encounters. A lack of energy, tiredness and heightened tension may be to fault for much of this.
There is a possibility that men who suffer from sleep apnea, a respiratory condition that causes disruptions in sleep, have an additional element contributing to their sexual decline.
• Makes You Age Faster
If you don’t get enough sleep, your body will produce more of the hormone cortisol, which is associated with stress. When present in high enough concentrations, cortisol has the potential to degrade skin collagen, the protein that is responsible for maintaining the smoothness and elasticity of the skin.
After a few nights of insufficient sleep, the majority of individuals have noticed that their complexion becomes yellow and that their eyes get puffy. However, it has been found that not getting enough sleep regularly can result in dull skin, fine wrinkles, and dark bags under the eyes.
Lack of sleep also prompts the body to secrete an insufficient amount of human growth hormone. Human growth hormone is responsible for the rapid development that occurs in our younger years. As we get older, it assists in building up our muscular mass, making our skin thicker, and fortifying our bones.
• Causes You to Gain Weight
When it comes to one’s overall body weight, it’s possible that sleeping more results in a smaller weight loss. It would appear that a lack of sleep is linked to an increase in hunger as well as appetite, as well as perhaps leading to fat.
A study found that those who slept for seven to nine hours each night had a nearly 30 percent lower risk of becoming fat compared to those who slept for less than six hours per day.
Recent studies have focused on the correlation between getting enough sleep and having enough levels of peptides that control hunger.
Ghrelin causes appetite to increase, unlike leptin, which sends a message to the brain that it is full and suppresses appetite. Decreases in leptin are connected with decreased sleep time, while increases in ghrelin are associated with decreased sleep time.
What Are the Early Signs of Lack of Sleep?
Always listen to your body because it usually sends you signals beforehand when something is wrong. If you’re experiencing a lack of sleep, be on the lookout for the following signs:
- You have trouble focusing on the tasks that seemed natural until now (like cooking or driving).
- You feel too tired to participate in daily activities.
- You become irritated and feel like arguing over every little thing.
- Even the smallest noises are highly annoying.
- You don’t find joy in the things that used to make you happy.
- Your school and work performance is decreasing.
- You’re experiencing drastic mood swings.
Tips for Getting More Sleep
A proper sleeping schedule is something that a lot of people struggle with. In an attempt to help you improve the quality and duration of your sleep, we’ve put together some tips that you might find useful.
• Adopt a Consistent Wake Up Schedule
You should set your alarm for the same time every day, even on the weekends and holidays. Waking and getting out of bed the same time every day can improve the quality of your sleep at night. Maintaining a consistent yearning for sleep throughout waking is facilitated by adhering to a regular wake time.
This sleep urge gradually builds up, and if you cut it short by sleeping in later than usual, it will be more difficult to get to sleep the following night. It’s a lot harder to get up early on Monday morning if you spend the weekend sleeping in later than usual.
Before going to bed, engage in some type of activity that will help you unwind and relax, such as getting into a warm bath or reading a book.
You can condition yourself to associate these activities with sleep if you make them a regular component of your routine before night, such as a routine that includes reading or listening to music. Because of this connection, falling asleep should be an easier process for you.
• Set Up the Proper Bedroom Atmosphere
Maintain a comfortable temperature in the space, together with its darkness and silence. It is possible that being exposed to light in the evening will make it more difficult to fall asleep.
Avoid using light-emitting screens for an extended period right before going to bed. Think about utilizing earplugs, white noise machines, sleep masks, or any number of other tools to create an atmosphere that caters to your specific requirements.
It’s possible that engaging in relaxing activities like taking a bath or practicing relaxation techniques right before bed will help you get a better night’s rest.
• Eat a Proper Breakfast
In addition to numerous other health benefits, having a balanced breakfast can assist your body in waking up and getting moving by signaling that it’s time to do so. In contrast, a lack of food at the start of the day might disturb your blood sugar rhythms, decrease your energy, and raise your stress levels.
• Don’t Nap for Too Long
It is essential to practice caution when taking naps to improve the quality of sleep experienced at night. It is possible to throw off your normal sleep schedule and make it more difficult to fall asleep when you want to if you snooze for an inordinate amount of time or too late in the day.
The ideal time for a nap is just after lunch in the early afternoon, and the optimal length of a nap is somewhere in the neighborhood of 20 minutes.
Products to Help You Sleep
• Sleep Mask
Eye masks can be a part of a relaxing nighttime routine that prepares your brain to recognize that everything is secure, tranquil, and comfortable. This can help you get better sleep.
Your usual activities signal to the brain that it is time to wind down and give way to sleep. The amount of sleep you receive may increase if you use a sleep mask because they make it easier to nod off sooner.
The elimination of light is the fundamental objective of wearing a sleep mask. The body’s circadian rhythm is heavily influenced by shifts in the amount of light that occur during the day, which also affects alertness and sleep.
Alterations in one’s mental state, bodily state, and behavior can be attributed to the circadian rhythm, which occurs continuously for 24 hours. It is sensitive to the dark as well as the light.
The times when a person is most sensitive to light are approximately two hours before their typical bedtime and approximately one hour after they wake up. A person’s circadian rhythm can be disrupted when they are exposed to light at this period, which can make it difficult for them to go asleep or remain asleep.
Using electronic gadgets, as well as any other source of light during the night, might make it more difficult to fall or stay asleep. Blocking away the light that would normally prevent a person from falling or staying asleep is one of the primary functions of sleep masks.
A sleep mask can also be used in the morning to assist block light that could potentially wake a person up before they are properly rested and ready to go up.
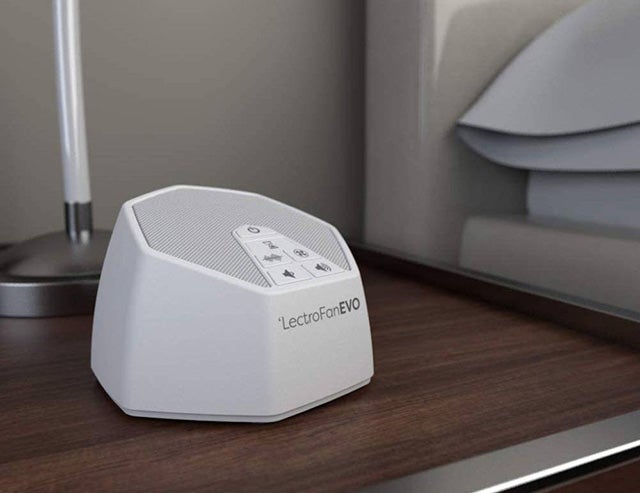
• Sound Machines
People turn to sound machines for various reasons, but one of the most prevalent is covering up unwanted sounds. Especially for those who have to cope with noisy pets, spouses, or other noises in their environment. One of the most significant factors that prevent one from sleeping is noise.
Some people are more likely to be distracted by distracting noises when they are present in an environment that is too quiet. Your hearing will become more sensitive when the environment becomes quieter.
When it is too quiet, you can pick up on everything and give it significance, which almost always results in you becoming agitated over the noise and being unable to sleep because of it.
One of the most common manifestations of this phenomenon is the inability of someone accustomed to sleeping in a metropolitan setting (which typically has higher levels of background noise) to fall or stay asleep when they travel to a more rural area (with less ambient noise). It may feel as though snores coming from a companion are getting louder.
Even if a sound machine won’t completely get rid of those annoying noises, it can help you focus less on them and enjoy your time more. This sound machine can divert your attention away from such noises.
• Sleep Aids
Sleep aids that don’t need a prescription can be helpful for a night or two here and there when you just can’t get to sleep. But there are a few important qualifications.
Antihistamines are found in the vast majority of sleep aids that do not require a prescription. It’s possible to rapidly build up a resistance to the sedative effects that antihistamines have. When used for a longer period, there is a decreased likelihood that they will cause drowsiness.
In addition, some over-the-counter sleep aids have the potential to make you feel drowsy and ill the following day, while others require a doctor’s prescription. This is what people refer to as the “hangover effect.”
It is also possible for medications to interact negatively with one another, and there is still a lot that is unclear regarding the safety and efficiency of over-the-counter sleep aids.
You might want to check: A Better Life Starts with Healthier Sleep Habits
The Verdict
Sleep is critical for everyone, regardless of age, according to scientific research. A good night’s sleep is the key to a healthy mind, body, and spirit. Getting a good night’s sleep is the simplest and most effective treatment for sleep deprivation.
If you haven’t had a good night’s sleep in a while, it can be a challenge to get back into the swing of things. After this, you may require the assistance of your primary care physician or a sleep medicine specialist, who can perform a sleep problem diagnosis and provide appropriate treatment.
Photo credit: Just dance/Shutterstock; Vitalinka/Shutterstock;
Realstock/Shutterstock; Prostock-studio/Shutterstock;
FotoDuets/Shutterstock; gontabunta/Shutterstock;
Ground Picture/Shutterstock; oatawa/Shutterstock;
RollingCamera/Shutterstock; Andrey_Popov/Shutterstock;
fizkes/Shutterstock; Sergey Chumakov/Shutterstock;
Phoenixns/Shutterstock; favorita1987/Shutterstock;
l i g h t p o e t/Shutterstock; AJR_photo/Shutterstock;
Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock; Ground Picture/Shutterstock;
BLACKDAY/Shutterstock; Roman Chazov/Shutterstock