If somebody would ask you to mention the major organ systems in your body you would probably think about digestion, the productive system, circulatory and respiratory systems, and all the others that you’ve learned about in your biology classes. However, back in the 1990s, Dr. Matsuda discovered something that we today referred to as the endocannabinoid system (ECS, for short). If you’re wondering what that is and what role it plays in the human body, we are here to shed some light on the situation.
What Is the Endocannabinoid System?
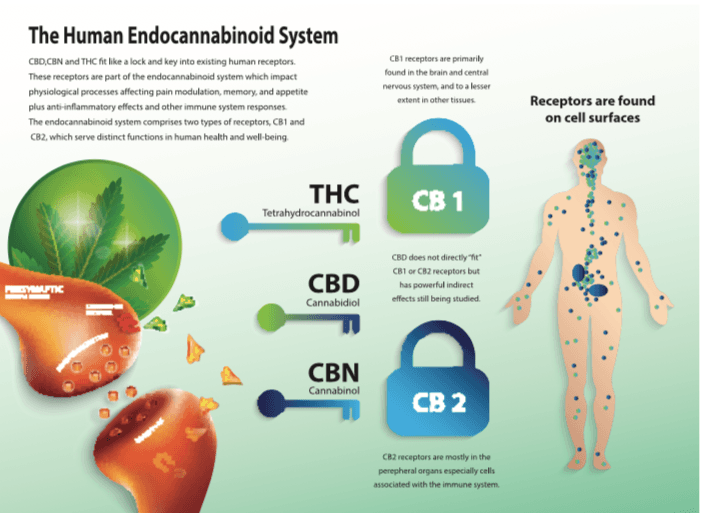
The endocannabinoid system is present in the human body regardless of whether you use cannabis or not. In order to further understand how this works, we need to refer to the three main components of the system.
#1: Endocannabinoids
The first component is known as endocannabinoids. These are molecules that the body produces and even if they are similar to the ones found in cannabis, they’re natural because they are bodily made.
Researchers have identified two major endocannabinoids up to this day: AEA (anandamide) and 2-AG (2-arachidonoylglycerol). These two components are responsible for making sure that the internal functions of your body are running smoothly. The body only makes these as needed, so scientists have here to figure out what are the normal levels of each.
#2: Endocannabinoid receptors
As far as endocannabinoid receptors are concerned, the first major category is found in your central nervous system and it is comprised of CB1 receptors, while the second category is part of your immune cells which means it can be found in your peripheral nervous system, and it is comprised of CB2 receptors.
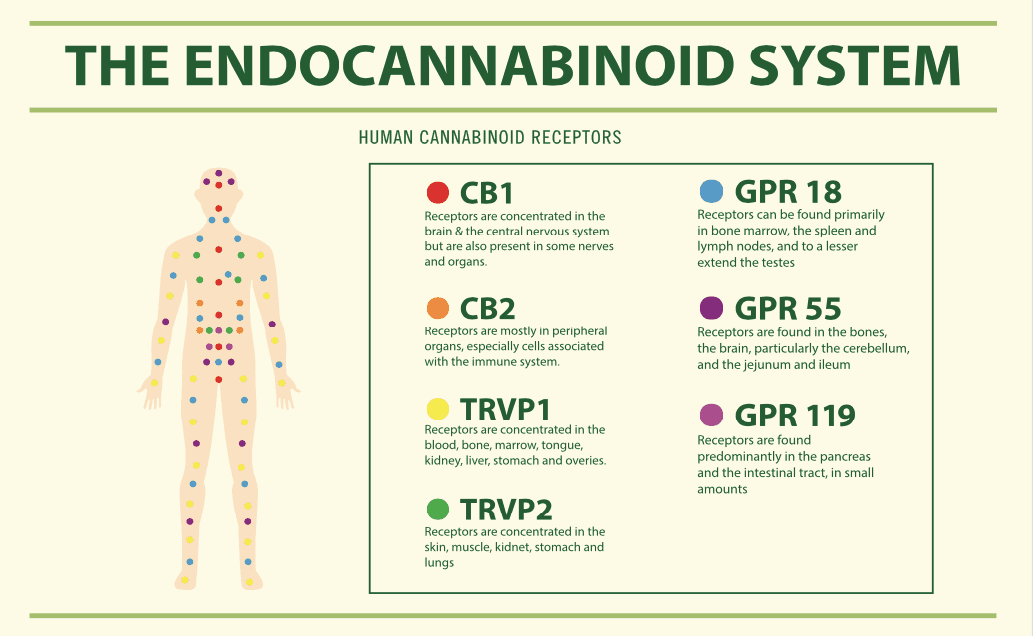
#3: Enzymes
Once the endocannabinoids inside the body have fulfilled their function, enzymes will kick in to break them down. The two major enzymes that are responsible for the breaking down process are fatty acid amide hydrolase and monoacylglycerol acid lipase.
Fact About the Endocannabinoid System
Even if you’re not interested in the scientific explanations and medical details behind this system, you should know that ECS is basically responsible for tuning the human body’s basic physiological functions. Because it is linked to homeostasis, the system will have an impact on different bodily functions as it helps regulate them making sure they properly interact with one another.
- Even if it was recently discovered, the ECS has been part of the world for about 600 million years. Cannabinoid receptors have been discovered in sea-squirts and basically every vertebrate and invertebrate have it.
- Your body has a lot more endocannabinoid receptors than you can possibly imagine. In fact, scientists believe that these receptors outnumber the neuromodulatory receptors in the body. Anandamide alone is found in great numbers throughout the brain and it plays a crucial part in keeping your central nervous system healthy.
- Because ECS is very important in regulating body functions, it is perfectly normal for people who are ill to experience changes in the system’s activity. So far, evidence has shown plenty of diseases (from arthritis to cancer) will change the levels of endocannabinoids in the human body, which means that ECS could pose a target for promoting good health.
- It is no secret that marijuana and hemp were often used in the past as a treatment for many different problems, such as depression, arthritis, and epilepsy. Back in the day, people were not entirely sure why these plants were effective, but as researchers started digging more into the matter, they revealed more and more of the potential benefits of using cannabis as medicine.
Enzymes, Receptors & Cannabinoids
We previously mentioned that two of the components of the endocannabinoid system are receptors and enzymes, but how are they related to the effects of cannabinoids? What happens inside the body when someone smokes marijuana?
The plant has a cannabinoid that will bind to the CB1 receptor located in the brain and create that sensation of being “high”. That cannabinoid is known as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC, for short) and it is one of the most common ones found in cannabis plants. Your body also produces a more natural version of this cannabinoid (which is the anandamide we previously spoke of).
What’s interesting to note here is that tetrahydrocannabinol and anandamide are quite similar, yet the latter doesn’t give you the sensation of being high like the former one does. However, anandamide does have a calming effect on the body, nevertheless. The difference between the two sensations provided by each of these cannabinoids lies in the FAAH enzyme.
The primary role of this enzyme is to break down your body’s natural endocannabinoids, but it doesn’t manage to do the same with THC. As a result, the effects that THC has on the body are way more powerful and they stick to your body for a longer period of time.
If we were to examine the brain, we’d notice that both cannabinoids and endocannabinoids work in a similar fashion. They are both neurotransmitters that help pass the information on from one cell to another. There are different interactions between neurotransmitters and receptors, which also translates into a variety of different effects.
You might have heard a lot about cannabidiol (CBD) and the attention it’s been getting due to its controversial use and effects. What you should know is that CBD doesn’t have any psychoactive impact on the brain, which basically means that you can get the usual benefits of cannabis without the “high” that these usually provide.
One of the roles that CBD is known for is its capacity to block the FAAH enzyme from breaking down anandamide, which automatically makes this endocannabinoid more powerful. Because of that, CBD is now being used in the treatment of anxiety disorders.
What Is Endocannabinoid Deficiency?
When the endocannabinoid system isn’t functioning properly, there are multiple other systems that are affected by this. Medical science has named this condition “endocannabinoid deficiency” but this isn’t a disease itself, but rather an underlying condition for problems that include migraines, fibromyalgia, and even irritable bowel syndrome.
Since these conditions have proven to be resistant to a lot of different forms of treatment, specialists are now researching how cannabis-based treatments might be more efficient. Because the conditions are actually the results of several different systems in your body not functioning properly, it makes sense to consider that they are all tied to the complex endocannabinoid system.
Figuring out what the best course of action is from a medical point of view is still something that needs a lot of research, but that is what got CBD products to be considered as a viable treatment option by patients. Of course, there is still a lot more research to be done in this area in order to discover how endocannabinoid deficiency can be treated.
What’s interesting is the fact that cannabinoids are now being considered a good treatment option even when a patient’s problems aren’t always related to endocannabinoid deficiency. The medical world is currently researching how these could be useful for cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, chronic pain and chronic inflammation conditions, neurological problems, and even Alzheimer’s disease. At the time being, CBD is being used as a treatment for conditions that include asthma, pain, pediatric epilepsy, and others.
Endocannabinoid System & Sleep
So far, the studies that have been conducted to identify the link between ECS and sleep were focused on rats and how their systems interacted. As far as researchers have been able to figure out so far, the central nervous system can pick up increased endocannabinoid signaling which helps promote sleep-inducing effects.
On a more scientific level, here is what researchers have discovered as far as the relationship between ECS and sleep is concerned:
- When anandamide has been administered in rats intracerebroventricularly, they showed signs of the sleep-inducing effects, while their slow-wave and REM sleep was increased. That means that anandamide plays an important role in helping reduce wakefulness and helps transition to other stages of sleep.
- The administration of anandamide in the basal forebrain led to increased levels of adenosine. Adenosine is an organic compound that acts upon your brain as an inhibitory neurotransmitter. It basically calms down the central nervous system and suppresses arousal while also inducing a state of sleep. Every hour that you spend awake, the levels of adenosine in the brains rise further.
- When experiments on rats were focused more on sleep deprivation, the expression of their CB1 receptors was on the rise in the central nervous system, indicating a further connection between sleep and the endocannabinoid system.
Cannabinoids & Sleep
For plenty of people, it all comes down to the following question: Can cannabis help me sleep better? The answer to that question is more complex than you think, and the best we can do is tell you how things stand from a medical point of view.
Cannabis is considered a very controversial sleep aid, but it’s something that many people who are experiencing sleep disorders are willing to try. There are plenty of supporters to medical marijuana and people claim that it can successfully restore the natural sleep cycle. As always, we can tell you that while cannabis might be a viable solution if you are sleep deprived, it’s not something that everyone should try, and we will explain why.
Marijuana is of many different types, and this is very important for you to know if you’re considering it because some types can actually energize you instead of calming down your central nervous system. It all comes down to the actual cannabinoids that are in the plant, two of the most common ones being:
- CBD (Cannabidiol) which is now widely used because it offers the benefits of cannabinoids without the sensation of being high.
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) which acts like a psychoactive drug that may alter reality.
Comparing these two on a molecular level, THC is better at helping induce sleep compared to CBD. A study conducted in 2008 revealed the fact that high levels of THC can actually decrease the amount of REM sleep a person gets. In translation, it makes you dreamless, and if you are a person with PTSD, that could automatically mean fewer nightmares and better sleep quality.
Theoretically speaking, the consumption of THC can lead to more deep sleep, but is that always a good thing? REM sleep plays a very important part in our sleep cycle because it helps restore our immune system and our cognitive functions, so getting less REM sleep can actually impair sleep quality in the long term. One thing is for sure: marijuana changes your sleep cycle.
One of the most important things that you have to remember is to never experiment with these drugs unless you are advised by your doctor to use medical marijuana. While it can be useful in treating insomnia, there are always the legal implications to consider, and while medical marijuana is allowed in some corners of the world, it is very much still an illegal drug in others.
Conclusion
The endocannabinoid system plays a very important part in regulating other bodily systems. Even so, this is a topic that is still subject to very intense research because specialists have yet to identify the exact correlations between every one of your body functions and ECS. It is becoming clearer that ECS can help regulate sleep patterns through the endocannabinoid known as anandamide, as many studies conducted on rats have shown so far.
However, there is always a delicate topic of medical marijuana consumption to consider if you are suffering from different types of sleep disorders. Insomnia is something that affects people on a global level, yet medical marijuana is still not an option in most countries in the world. This is why you should never consume these drugs unless you have a medical prescription to do so, as the side effects and legal implications might not be worth it.